| |
 |
Numerical Example |
 |
|
|
|
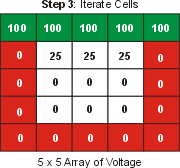
Now we iterate the equations according to a relaxation algorithm.
If the medium of the square is homogeneous (i.e. the material properties
do not change) then, according to the discrete form of Laplace's
equation, the value in each square is equal to the average of its 4
neighboring voltages. Thus, we average all of the neighboring
voltages together and place this value in the array. This is the
first iteration. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note that not much has changed. It will take several iterations
before the voltages at the bottom will be non-zero. Slowly, but
surely, the relaxation algorithm will converge on the physical solution. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
