|
| |
| |
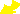 |
Vertical Polarization |
|
|
| Linear polarization is the simplest case of uniform plane wave propagation. One example -- vertical polarization -- is animated in the case below. |
|
|
|
| Notes: |
|
- In all these diagrams, the central arrow with the large arrow head is the direction of plane wave propagation. The dark arrows represent electric field intensity and direction and the light arrows represent magnetic field intensity and direction (as measured from the point at the base of the vectors). Note that all vector types are mutually orthogonal for all types of plane waves.
|
| |
- This animation shows one "equi-phase front" of a uniform plane wave. In this plane, all of the fields are synchronized and time-harmonic; they beat in-phase at the same frequency.
|
|
- By convention, terms describing polarization ("horizontal", "vertical", etc.) are usually based on the behavior of the electric field. Thus, we speak of vertical polarization even though the magnetic field has a horizontal orientation in space. Likewise, we speak of horizontal polarization even though the magnetic field has a vertical orientation in space.
|
|
|