
Final project: The Martian Network
2. Basic Information about Mars
Out of nine planets in our solar system planet Mars is the fourth one, behind Mercury, Venus and Earth, in terms of the proximity to the Sun. Since the rocks, soil and sky have a red or pink hue it is commonly reffered to as the Red Planet. It was named after the Roman god of war.

An ilustration of the planet Mars and its interior structure.
It's radius is about half of the Earth's at 3397 km, while its mass amounts to only about 1/10 of the Earth's. The length of a day on Mars is 24.6597 hours and its sidereal rotation period 24.6229 hours. As it is further away from the Sun as the Earth, its orbit around the Sun is almost twice as long as the Earth's and equals 686.97 days.
We are going to be very much interested in the distance between Earth and Mars at different times of their orbits. The maximum distance between the two plantes is 401.3 million kilometers, while the minimum distance is considerably smaller at 55.7 million kilometers.
The variations in temperature on the Martian surface are very high. The average temperature on the surface is 218 K (-55 C, -67 F) and it can range from as little as 140 K (-133 C, -207 F) at the winter pole to almost 300 K (27 C, 80 F) on the day side during summer.
Martian topology is very diverse. On a topography map of Mars below, we see that the northern hemisphere is relatively low for the most part, while the southern hemisphere is considerebly higher and strikingly diverse. The altitudes can range from -4 km to over 25km high volcano peaks in the Tharsis region. One should bear in mind that there is water on mars and hence no sea level. Therefore the 0 altitude surface must be chosen somehow, for instance "mean gravity surface".
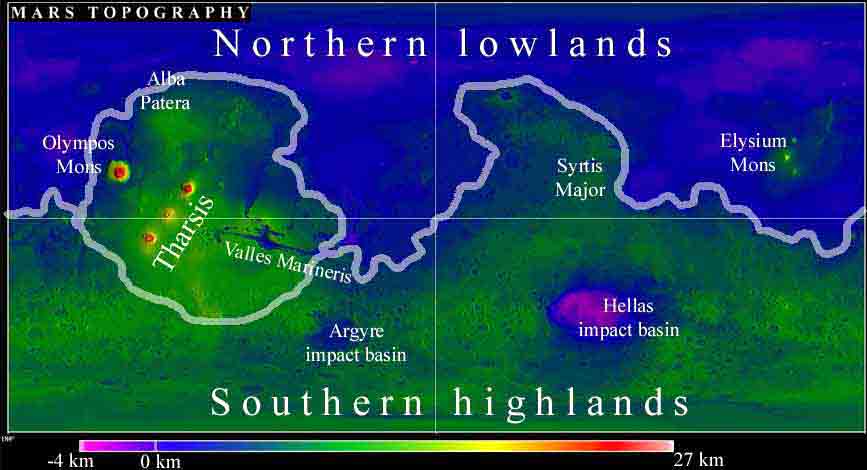
The topology map of planet Mars.
For other basic parameters and information about Mars, we refer
the reader to:
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/factsheet/marsfact.html
Next section: Satellite constellation