Astro-Location (RFID Interrogator)
| RFID Waypoint | RFID Interrogator | Portable Array |
The
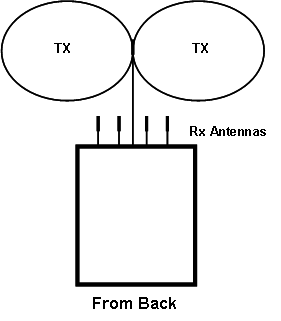
Lunar Astro-Track RFID interrogator is made up of 5 dipole antennas:
One for transmission and four for reception. The four receiving
antennas are used together as a phased array to perform DF.
The
transmit antenna situated above the receiving elements to achieve a
better line of site to the RFID and to minimize leakage into receive
antennas. Behind each of the receive antennas a very narrow, deep
notch filter is used to null out RFID tone (could be a stub). Due
to the spread spectrum nature of the RFID waypoint waveform, this
nulling will have a minimal affect on the ability to detect a RFID
waypoint even though it is in the same band.
Periodically the interrogator will send out short duration bursts of energy at 1.15 GHz to activate the RFID Waypoints. After
a RFID is powered up by incident pulse from the interrogator, it will
immediately transmit a direct sequence spread spectrum sdignal.
The signals spreading sequence will be unique to a paricular
waypoint. When an RFID's return signal is detected, the return
time and interrogation burst time are used to compute the range ring.
The thickness of the range ring is adjusted by cross-correlation
levels, a priori system noise knowlege, and timing uncertainty.