The rectenna is a grid array of patch antennas, which collect the RF energy, rectify it, and transfer it to a central collection station. Rectenna efficiencies are reaching 85% in the lab, and we expect that this will be commercially viable by the time the rectennas are constructed.
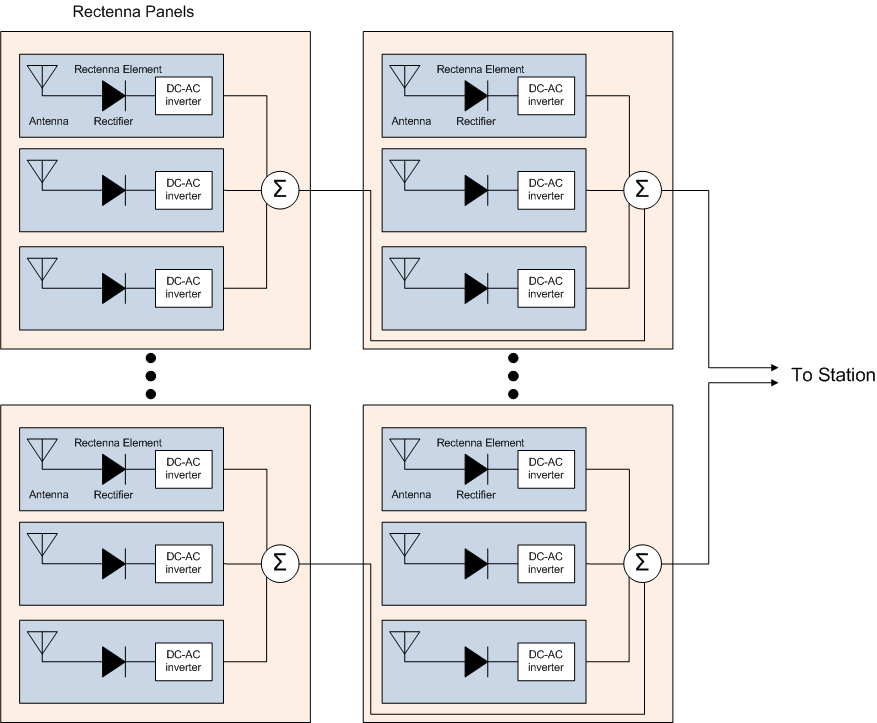
Figure 1. Rectenna block diagram.
The rectenna's primary factor is its effective aperture. The ability to capture energy efficiently is not dependent on directivity, but on physical aperture and construction. Of the various antennas designs considered, dipoles provide the most efficient energy harvesting as their effective aperture is larger than their physical aperture. Conversely, dish antennas have effective apertures smaller than their physical aperture and thus do not make good rectennas.
A patch antenna is similar to a dipole; instead of a wire suspended in space, it is a rectangle of metal suspended above and parallel to a ground plane. Patch antennas are economical as they can be constructed using printed circuit boards. Additional components, like the rectifier, can be printed on the same circuit board. Patch antennas offer the benefits of aperture efficiency near that of a dipole while being the most economical to construct.
We have selected patch antennas for the rectenna design because they have both great aperture efficiency and low cost. The dimensions of the patch antenna will be a quarter wavelength square, or 1.3cm x 1.3cm.

Figure 2. Patch Antenna
A panel of patch antennas spaced in half-wavelength increments is placed on a large panel containing 10,000 rectennas, for a total dimension of 1.3m x 1.3m (1.7m2). The power from all the rectennas is rectified, combined and converted to a low-frequency AC signal for less loss in transmission over kilometers of distance to a central collection facility. Here the power from all the rectenna panels is combined and deliver to the grid. To reduce redundant cables, the rectenna panels are daisy chained.
It will take 339 panels to fill the main beam of the satellite constellation. The panels should be placed as close to each other as practical, leaving space for maintenance.
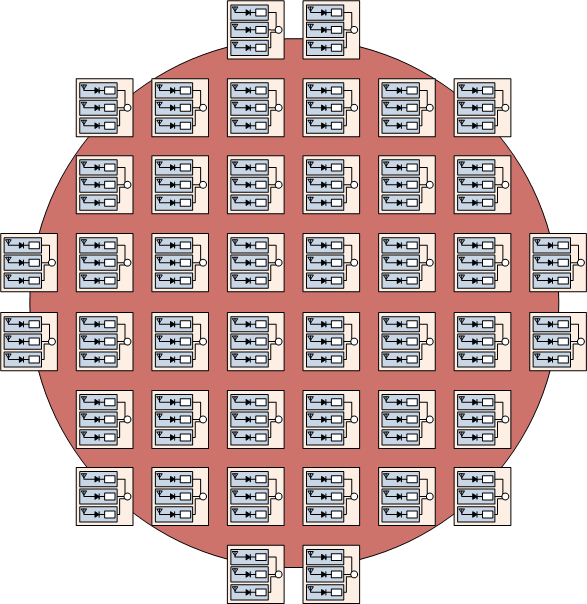
Figure 3. Panel placement to maximize collection of main beam from satellite constellation.