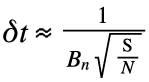Location Systems
Location Systems
Simulation of the Dilution of Precision (DOP)
Dilution of Precision describes the geometric strength of a satellite configuration for position accuracy. In this Maritan Global Positioning System, Positional Dilution of Precision (PDOP) is used to assess the geometric quality of the satellite constellation. Simulation results of the chosen orbital constellations indicate that the average PDOP value is 4.473 m (see orbital mechanics). The table below shows the horizontal, vertical, and geometric DOP.
HDOP |
VDOP |
GDOP |
2.207 m |
3.875 m |
4.91 m |
Position Error Calculation
Since the primary constraint on the system is the +/- 5m accuracy, this constraint was set as a worst-case value and the other parameters were back-solved. This ensures that the system will meet the design specifications.
For the Mars network, the number of satellite in view varies between 4 and 6, and the signal strengths also vary depending on the elevation angle of the satellite and the orientation of the receiver [1]. The C/A code will be modulated using BPSK. The following calculations assume that averaging is used under worst-case scenario conditions.
Bn = Bandwidth = 2.5 MHz after filtering |
|
The above calculations find that the receiver noise error is 4.73 meters.
Uncorrected Total Error
From this point, the total error calculation is trivial. The errors used in the calculations are shown below.
Satellite Clock Error |
σc |
3.5 m (same as Earth GPS) |
Ephemeris Error |
σe |
4.3 m (similar to Earth GPS) |
Receiver Noise |
σn |
4.73 m (calculated above) |
Tropospheric Delay |
σt |
0.0135 m (based on Mars' tropospheric density compared to Earth's (1/148th)) [3] |
Selective Availability |
σsa |
0 m (none on Mars) |
Ionospheric Delay |
σi |
Negligible [3] |
Multipath Error |
σm |
Negligible |
The total positional error is the sum of the squares of the errors, yielding an uncorrected error that is lower than that of Earth's GPS.
![]()
This error can be reduced by using intelligent correction techniques to reduce clock error and ephemeris error [2]. The Martian Global Positioning System uses frequent clock synchronizations and ephemeris correction signals to overcome these errors.
Position Estimate
For the Martian Global Positioning System, the average time to collect sufficient measurement observations to compute a prescribed accurate position is given by:
δt = rms timing error |
|
The rms timing error is δt = 0.3726μs. As with a typical GPS receiver, the Martian GPS receiver will also update the display no more than twice per second, so the pulses can be averagd over a period of a half second, which will decrease the rms error by the square root of 500 to an rms value of 16.81ns [1]. The worst-case rms distance error is then found to be 5 meters.
![]()
Link Budget
The following values are used to calculate the communication link for this MPS.
Bn = Bandwidth = 2.5 MHz after filtering |
Solving for Pt = 8.863dB = 7.7 Watts |
This means that the satellites only need to broadcast 7.7 Watts to maintain sufficient positional accuracy. This power level is reasonable and can easily be incorporated into the power budget.
[1] T. Pratt, C. Bostian, and J. Allnutt, Satellite Communications, 2nd Ed., pp. 475-476, 2003.
[2] D. J. Bell et al, “Mars Network: A Mars Orbiting Communications & Navigation Satellite Constellation”, Deep Space Communications and Navigation Systems Symposium, Pasadena CA, 1999.
[3] http://ipnpr.jpl.nasa.gov/progress_report/42-149/149C.pdf
Images: [A] http://cndyorks.gn.apc.org/yspace/articles/gps_upgrade.htm