
Venus
This page provides some characteristics of the planet that are relevant for our mission and will constraint our design choices.
Orbit
Venus is the second planet of our solar system. At a distance of 108 millions of kilometers from the Sun, It takes her 224 days to complete a rotation around the Sun.
Venus has the particularity of having a retrograde rotation,
completing a rotation in 243 days, in the opposite rotation direction from the Earth and the other planets of our solar system.
When getting closest to the Earth, 40 millions of kilometers keep the two planets apart.
More information can be found here.
Atmosphere
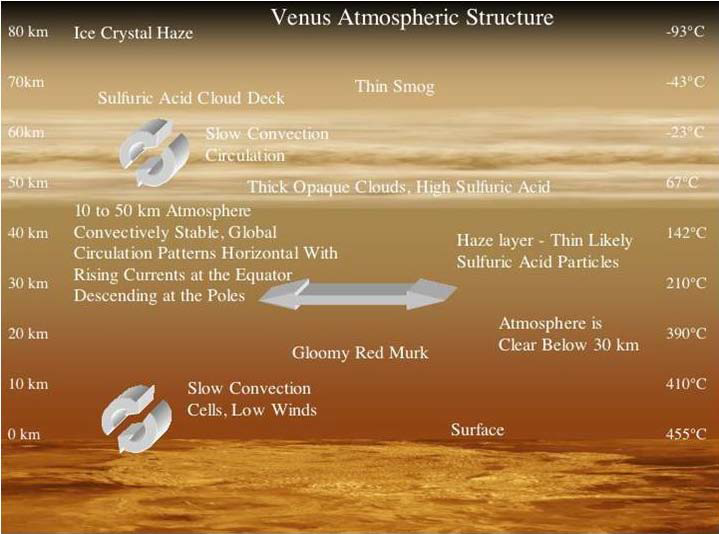
Venus has a very thick atmosphere, with a pressure above ground of 92 atm. The composition is mainly CO2 (95%), with N2 and some sulfuric compounds (H2SO4 forming clouds, SO2). Also, the atmosphere contains some traces of water depending on the altitude. The temperature on the venusian surface is about 460°C.
Wind phenomena happen in the atmosphere. There are basically two wind regimes: A so-called Hadley cell at about 50-65 km altitude, and a subsolar to antisolar pattern at 100 km altitude, as shown in figure 3. The fastest winds are recorded at 70 km of altitude, at latitudes below 80°, for a speed of 100m/s, reducing to 40m/s at a 80° latitude [13]. The wind speeds at the poles are null, at least for altitudes between 45 and 60 km [14]. At the surface, the winds have a speed beteen 0.3 and 1 m/s [15]. Another source [16] reports velocities between 0.3 and 0.6 m/s.
Despite the thick atmosphere, it has been shown that the attenuation of waves (32 cm) is only of 8dB [9] (depending on the glancing angle). Indeed, the CO2 molecule constituing the major part of the atmosphere, is symmetric and possesses no dipole moment. The opacity of the atmosphere is of 84 ± 6 dB for 1cm waves [10]. A model has been developped in [11] which gives the total attenuation through the atmosphere with respect to wavelength and incidence angle (figure 4).
Because of this thick atmosphere, the net solar flux on the surface is only 20W/m² [17]. This seriously restricts the interest of using solar panels.
When transmitting EM waves through the Venus atmosphere,the refraction of the atmosphere has to be taken into account as well.
Geology
The venusian surface has many volcanoes covering its surface. Some evidence suggests that this activity is still ongoing. Volcanoes are spread rather uniformly over the planet, suggesting the absence of plate tectonics movement [8]. The surface of the planet is thought to be between 300 and 600 million years old.
However, little is known about the internal structure of the planet. It is believed to have a crust, a mantle and a core, just like the Earth. But little is known beside that. This is the main reason for our mission, as studying planet seismology will help at identifying the internal characteristics of Venus's geology.